This week Google announced that starting in January 2017, their Chrome browser will start marking HTTP sites that transmit passwords or credit cards as non-secure. For a while now, Google has been making an effort to get websites to convert their sites to HTTPS. With this announcement, they are making an even stronger push.
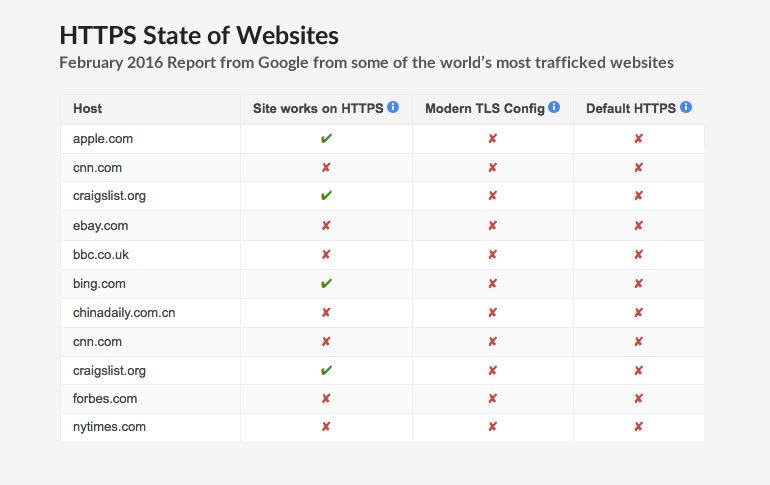
Why is Google doing this? According to Google, they want to make the Internet more secure. HTTPS (Hyper Text Transfer Protocol Secure) adds a layer of security to the standard HTTP protocol. The HTTP protocol is the set of rules for transferring files on the Internet (images, text, video, sound, etc.). With HTTPS, it means that all communication between your browser and the website you are on is encrypted. You see HTTPS on sites like Gmail, Facebook, Amazon, your bank, sites where you make credit card transactions, etc. but most sites are not HTTPS (even the majority of the top websites in the world are not). According to a February report from Google, 79 of the top 100 sites on the web (excluding Google owned properties) don’t deploy HTTPS by default. Additionally, 67 of those sites use either outdated encryption technology or don’t have any at all.
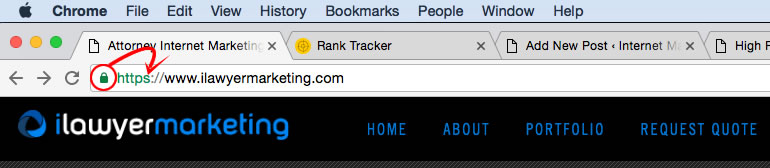
When browsing a website, you can tell if a site is secure by seeing the HTTPS protocol together with a green lock as shown in the image below. Also note the “s” after http:
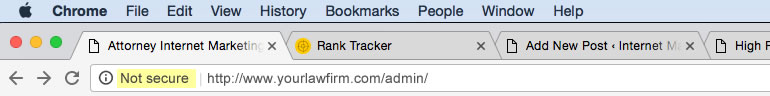
For most law firm websites, visitors will not notice any difference unless clients sign on to your site with a username and password. You should see this if you visit your login page in to your website since that requires a password. Below is an example of what this will look like. I added the highlight here so you can see the change that will be taking place. As you can see, it will display “not secure” before your website address.
One important takeaway from Google’s announcement was this statement:
“Eventually, we plan to label all HTTP pages as non-secure, and change the HTTP security indicator to the red triangle that we use for broken HTTPS.”
While we don’t know when, it’s clear that in the future, all pages of your site would be marked as not secure. To a visitor that would look something like this in the address bar:
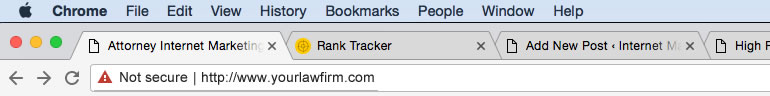
Notice that red warning icon? You see this warning icon today if you try to browse to a site on HTTPS that does not have a valid security certificate. This same icon is what Google is planning on displaying for any page in a site that doesn’t use HTTPS. That’s not something you want displaying to your site visitors as that is sure to stop potential clients from visiting your site which means this can cost you potential cases. I wouldn’t be surprised if they decided to display a warning label right in the search results, similar to how they mark sites with the “this site may harm your computer” message. You can imagine how that could negatively impact your CTR (Click Through Rates), which can be bad for site rankings.
Should you move your site to HTTPS?
You are going to need to do it at some point in the future, so it’s something you should consider. Here are the pros and cons:
PROS
Your site is more secure for your visitors – You have a contact form on your site and your visitors are filling out personal information when they submit on online case evaluation request. HTTPS adds multiple layers of protection including encryption, data integrity and authentication.
Higher level of trust – Sites that are on HTTPS have a higher level of trust from website visitors. Anything you can do to make sure your visitors more comfortable with sharing their information can help increase conversion rates.
Potential ranking boost – HTTPS is a ranking signal so you may get a ranking boost by moving to HTTPS. Google announced this back in 2014, so that’s a good reason to move to HTTPS right? In our testing, it is currently a minor factor but this is Google we are talking about. This could change overnight and considering their goal is to provide the very best user experience, it is highly likely this will become weighted heavier in future algorithms. A good experience to me is trusting the sites that I am visiting are safe to browse on and I’m sure you feel the same way. Google understands this and knows this is important to retaining and growing their already dominant market share of search.
CONS
When you move to HTTPS you change URLS – The biggest hesitation we have had in the past is not wanting to change URL strings. Whether you change to a new domain name or simply move your site to HTTPS you are still changing URL strings which means redirects come into play. In the past, Google has said that 301 redirects end up with roughly 15% loss of PageRank and others have reported the same. However, Google has said this is no longer true. Just recently Gary Ilyes of Google recently tweeted that 301 redirects don’t lose PageRank anymore.
Most experienced SEO’s that have been in the game a long time, myself included, know not to always believe what Google tells you. However, it’s something we are currently testing out. We even moved our site to HTTPS recently (along with other websites) and are monitoring results to see if there is any loss or improvement of rankings.
Acquiring and renewing SSL Certificates – Moving to HTTPS means that you need to get an SSL certificate for your website(s). If you have 5 websites, you will need 5 certificates. Prices range on SSL certificates and the specific type that you buy but for example GoDaddy prices these out at over $60 per year for one SSL certificate but there are less expensive options, even a free version from Lets Encrypt.
Setup process requires technical understanding – The setup process is a tedious and time consuming. It involved generating a Certificate Signing Request (CSR) and providing several pieces of information, using the CSR to order the SSL certificate, as well as configuring and installing the certificate on your server. This is something you need your IT person or your hosting provider to handle for you as some technical expertise is required.
Cost to Transition: Anytime you move your site, it’s a process to make sure the transition is handled the right way so you minimize any potential traffic loss or rankings drops. This means proper redirects from your old URLs to your new URLs, updating all references in your website that refer to anything non-https including your own site files and anything linking to an external source, update all links in your site, update sitemaps, updating Google analytics and Google search console among other things important. There is a cost to handle the required work here which will range depending on your provider.
TL;DR
Google Chrome will soon start labeling some websites that aren’t HTTPS as non-secure and in the future will mark all websites that don’t have HTTPS as not secure. As long as it’s handled correctly, the pros outweigh the cons here so we recommend transitioning your site to HTTPS.
Note: This is a service we are only providing to existing clients or new SEO clients.

